What is Scoliosis, and how you can test your child
What is scoliosis?
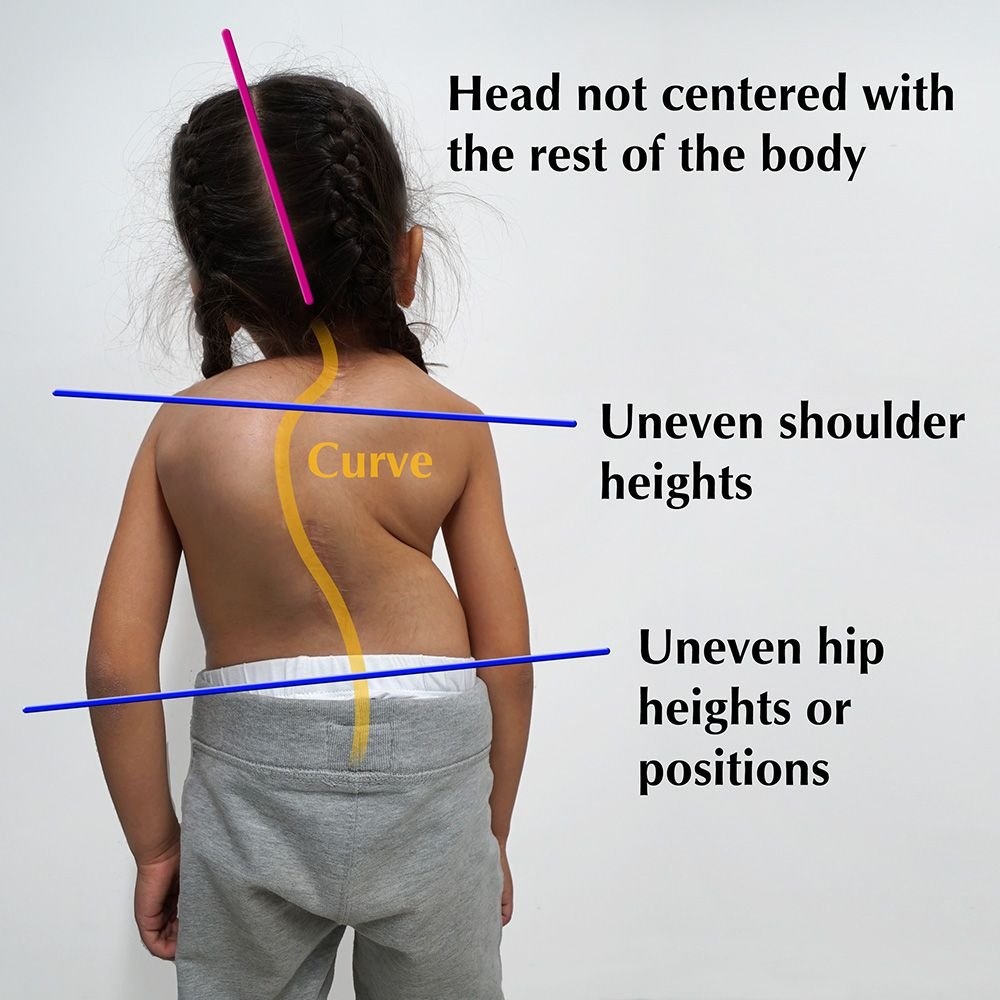
Scoliosis is a torsional condition that causes lateral curvature of the spine that is greater than or equal to 10 degrees cobb of idiopathic nature. Idiopathic means unknown cause. This results in asymmetry of the trunk and spine. It’s important to note this asymmetry as it can rapidly progress during periods of growth.
Figure 1: Back Pain - Scoliosis - Physio Frenchs Forest, Physio Macquarie Park
Figure 2: Back Pain - Scoliosis - Physio Frenchs Forest, Physio Macquarie Park
How to assess for Scoliosis?
Ask the individual to bend forwards. A positive test is given if one side of the thoracic spine or lumbar spine is elevate in comparison to the other.
A positive adams tests indicates a structural scoliotic curve. This is where the cobb measurement fails to correct past zero.
How do we measure severity of scoliosis?
Cobb angle is a measurement of the degree of side-to-side spinal curvature. A Cobb angle describes the maximum distance from straight a scoliotic curve may be. Generally, it takes at least 10 degrees of deviation from straight before scoliosis is defined
Mild scoliosis = 10-29° cobb angle
Moderate scoliosis = 30-49° cobb angle
Severe scoliosis = >50° cobb angle
Figure 3: Back Pain - Scoliosis - Physio Frenchs Forest, Physio Macquarie Park
Working alongside WiSE Specialist Emergency Clinic